SQL Server 2000 Tools
3. SQL Tools
Service Manager
SQL Server runs as a service on Windows NT Advanced Server and is usually configured to autostart. The SQL Service Manager can be used to start SQL Server running and must be run on the server itself. Simply bring up the window and press the buttons to start and stop the server.
SQL Service Manager

Other services may also be controlled by the service manager by selecting from the Services combo.
Enterprise Manager
The SQL Enterprise Manager is the administrative interface for SQL Server allowing the access to all of the features of SQL Server. SQL Enterprise Manager utilises Microsoft's Distributed Management Framework (DMF) so that any SQL Server installation can be controlled from Windows 95 or Windows NT workstation.
After registering a SQL Server installation on the SQL Enterprise Manager, the Server can be controlled through use of the outline control. Clicking on the Server will bring up an outline which contains the objects controlled by the server.
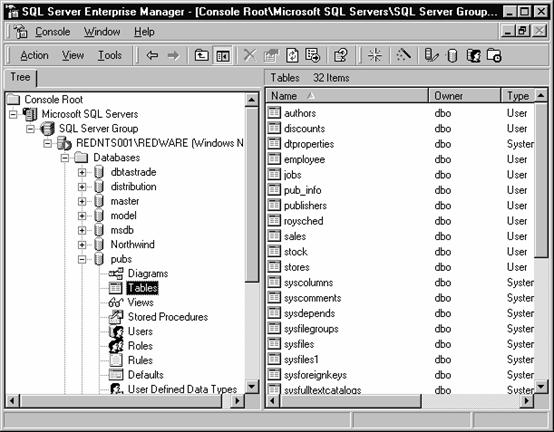
SQL Server Enterprise Manager
The Enterprise manager can be used to:
· Create a new database and alter database properties.
· Define new tables, views, stored procedures and user defined function within a database.
· Access tools such as the Query Analyser, SQL Profiler, and database diagrams.
· Define users and roles and set permissions on database objects.
· Schedule jobs with the SQL Agent.
· Set up and operate database replication.
· Import and Export data with the DTS.
· Perform database administration tasks such as backups.
· Monitor system activity.
Register the Server
Before we can change the structure of a database we need to register the Server on the current workstation.
This happens automatically the first time the SQL Executive is run or an option can be selected from the Server-Register Server menu to add additional servers.

Registering a Server
There may be several separate SQL Server installations running on the same machine.
SQL Query Analyser
The SQL Query Analyser is available from the TOOLS.. menu of the Enterprise Manager. The user must log onto the required server and specify the required database using the Database combo at the top of the window. The user can then type in a SQL Server statement in the Query window and press the Execute button to see the results interactively.
The Query Analyser can be used to run any command that SQL Server understands as well as standard SQL queries. Simply and type in the required Transact-SQL commands and press the Green GO triangle icon to run the query and view the results. Note that there are two pages for results, one for results sets returned and the other for messages.
Press SHIFT+F1 on any SQL keyword to launch SQL Books Online with the required information displayed.
SQL Query Analyser

Transact SQL commands can also be placed in a batch text file with a *.SQL suffix and executed from the OSQL window by selecting the File-Open menu and then executing the query. A batch file may have several sets of SQL statements executed with a “GO” command.
OSQL
OSQL is a command line utility which interacts with the database server from the DOS command prompt. It can be used to run jobs on the server from a windows standard batch file.
The following example logs onto the server as system administrator to query the authors table in the pubs database. The OSQL window is normally used to run a stored procedure.

